[ad_1]
To make this question clear, I suggest you to read about Java Reference/Object & method override first.
Below are the description of every steps in your code:
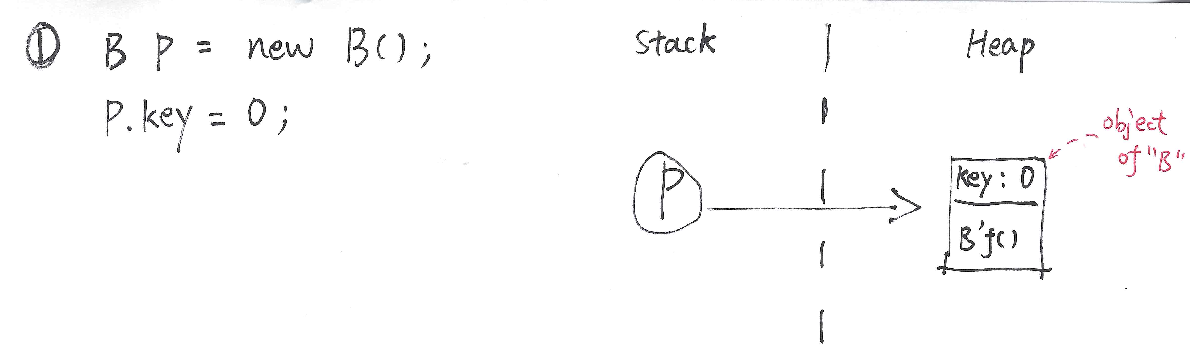
You create a new instance of Class”B” and a reference P pointing to it:

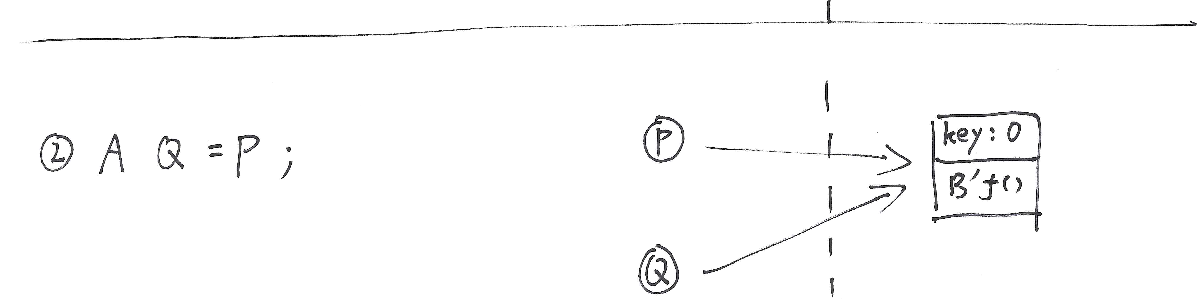
You create anoher reference Q and also pointing to above object:
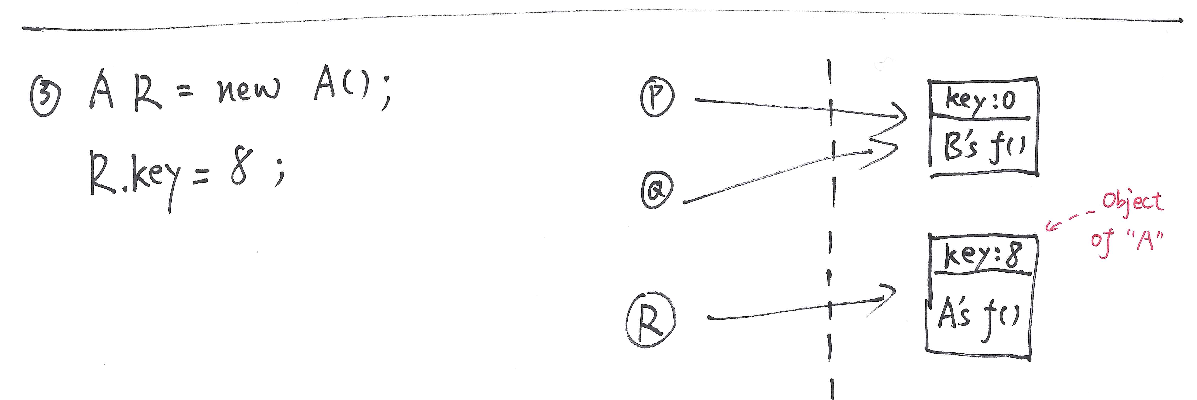
But pay attention, the methodf()in B overridedf()in A.

You create a new instance of Class”A” and a reference R pointing to it:

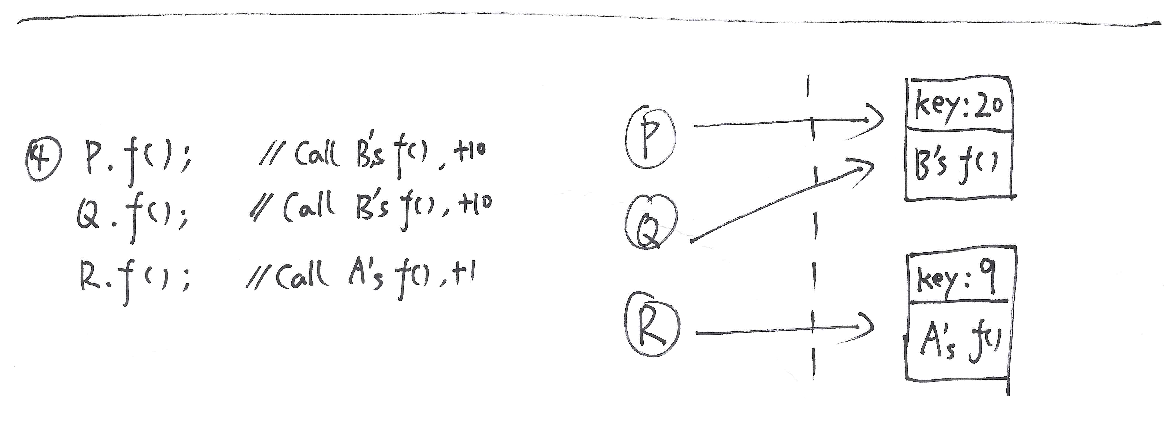
So, you have totally 2 objects(one for Class B and one for Class A) and 3 references now. Below code call B’s f() 2 times, A’s f() 1 times. So the result is:

[ad_2]
solved Can someone please explain the Outcome of the following code in java